Today, many enterprises have begun to use 3D printing technology to improve supply chain management, optimize production, and achieve agile manufacturing. With a history of nearly 30 years, FDM technology has a wide range of applications, not only for product prototyping, functional testing, but also for manufacturing tools and final parts, especially in the industrial, automotive and aerospace sectors.
3D printing will gradually be deeply integrated into the aerospace spare parts market and change the supply chain system of this market. The aerospace industry has a large number of parts and complex types. 3D printing technology not only meets the flexibility of obtaining spare parts "anytime, anywhere", but also saves the cost of keeping a large number of spare parts, simplifies inventory management and reduces the need for long-distance transportation.
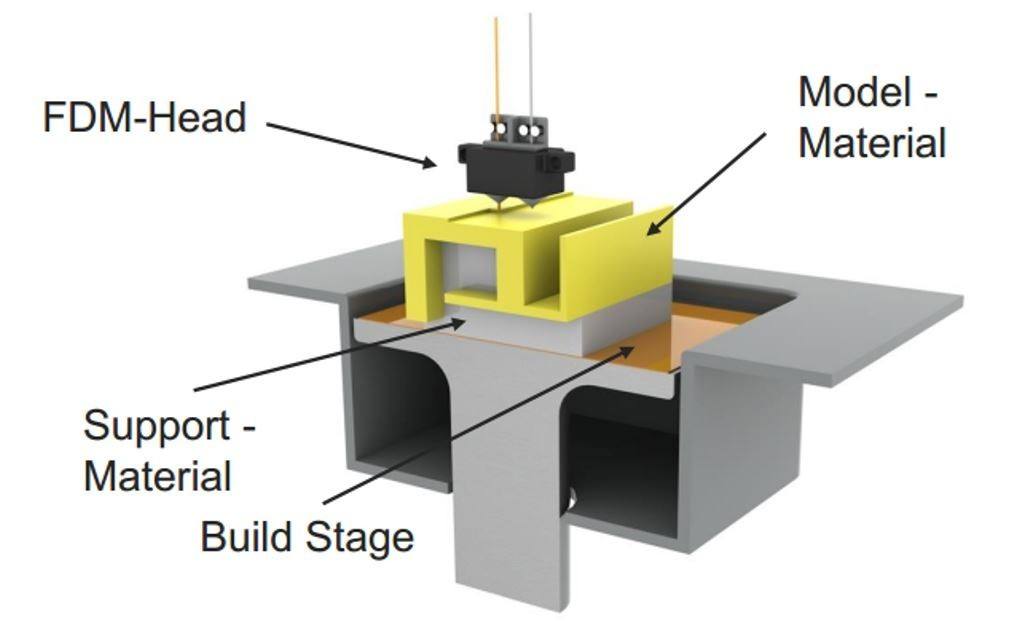
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a process of creating solid objects from digital models by depositing layers of material on top of each other. One of the most common types of 3D printing is FDM (fused deposition modeling), which uses a heated nozzle to extrude thermoplastic filaments onto a build platform.
FDM technology has many applications in various industries, but one of the most promising ones is in the supply chain system. Supply chain system refers to the network of activities, people, resources, and information involved in the production and delivery of goods and services from suppliers to customers. By using FDM technology, supply chain system can benefit from:
- Reduced inventory costs: FDM technology can enable on-demand production of parts and products, eliminating the need for storing large quantities of inventory and reducing waste and obsolescence.
- Increased flexibility and customization: FDM technology can allow for rapid prototyping and testing of new designs, as well as customization of products to meet specific customer needs and preferences.
- Improved efficiency and quality: FDM technology can improve the accuracy and consistency of products, as well as reduce the lead time and transportation costs associated with traditional manufacturing methods.
FDM technology is a powerful tool that can help supply chain system achieve higher levels of performance and customer satisfaction. By adopting FDM technology, supply chain system can gain a competitive edge in the market and create more value for their stakeholders.
3D printing has had a revolutionary impact on the manufacturing industry, allowing businesses to create objects quickly and efficiently. However, the advantages of 3D printing go far beyond manufacturing, as it can also help in the supply chain. One of the most popular types of 3D printing technology is FDM, which is commonly used in the industry. This blog will explore how FDM technology can aid the supply chain, how it might impact the supply chain for companies that do manufacturing, and the benefits of FDM 3D printing.
How 3D Printing Can Help in Supply Chain?
3D Printing can help the supply chain by allowing for the production of parts when and where they are needed. With 3D Printing, businesses can manufacture parts on-site, improving efficiency and reducing the need for transport. This technology also enables businesses to create spare parts, eliminating the risk of a production halt due to non-availability. The flexibility of 3D Printing makes it an ideal solution for supply chain problems, providing a faster and more cost-effective alternative for producing parts.
How Might 3D Printing Impact the Supply Chain for Companies That Do Manufacturing?
3D Printing technology will have a significant impact on the supply chain for companies that do manufacturing. Companies can use 3D Printing to create parts in-house, at lower cost and with greater speed, reducing lead times and increasing flexibility. The technology will also make it easier for companies to produce parts on-demand, reducing inventory cost and minimizing the risk of supply chain disruptions. 3D Printing technology will lead to a fundamental shift in manufacturing and the supply chain in general, making businesses more responsive and adaptable.
What are the Benefits of FDM 3D Printing?
FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) is one of the most commonly used types of 3D Printing technology. FDM technology offers several benefits, such as the ability to create complex geometries and parts with significant design freedom. It also allows for the use of multiple materials, including thermoplastics, composites, and metals, depending on the application. Another advantage of FDM 3D printing is the lower manufacturing cost as it reduces scrap and tooling cost, making it a popular choice in prototyping and small batch production.
How do you think 3D Printing Technology has Helped in the Industry?
3D Printing technology has profoundly impacted the industry, making manufacturing more flexible, efficient, and cost-effective. The technology has the potential to disrupt traditional manufacturing processes by opening opportunities for rapid prototyping, specialized designs, and customization of products economically. 3D Printing has also made the design and production process more sustainable by reducing waste and minimizing environmental impact. The technology is helping businesses overcome supply chain challenges and positioning them for a more prosperous future.
Conclusion
3D printing technology has significant potential to change the industry by making manufacturing more efficient, flexible, and economical. FDM technology offers a cost-effective and efficient solution to supply chain issues, reducing the need for transport, on-demand production, and improving adaptability. The benefits of 3D Printing extend well beyond manufacturing, revolutionizing supply chain systems and creating opportunities for businesses to innovate and stay competitive. With further developments and advancements in the technology, we can expect significant progress and growth in the industry.