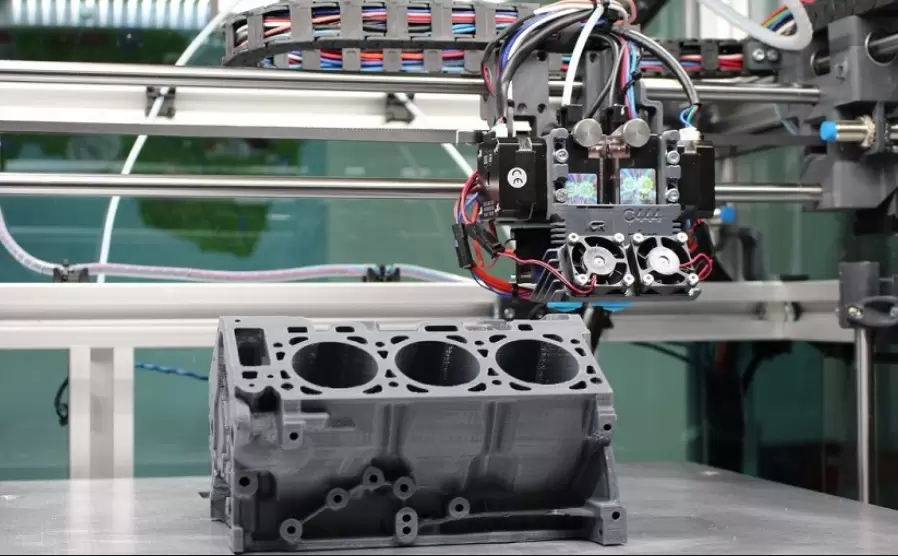
Material extrusion is a popular 3D printing process that uses a thermoplastic filament to create 3-dimensional objects. In this article, we will discuss the working principle of material extrusion, the materials used in additive manufacturing, the types of extrusion processes, and the advantages of this technology. We will also look at the applications of material extrusion in the production of various products.
Table of Contents:
I. Introduction
II. What is Material Extrusion in Additive Manufacturing?
III. Material Extrusion in 3D Printing
IV. Materials Used in Extrusion Process
V. Categories of Additive Manufacturing
VI. Types of Manufacturing Processes
VII. Examples of Extrusion Products
VIII. Other Names of Material Extrusion
IX. Products Made by Extrusion
X. Extrusion in Plastic Manufacturing
XI. Types of Extrusion Processes
XII. Advantages of Extrusion
XIII. Conclusion
I. Introduction
Material extrusion is a type of additive manufacturing that is used to create 3-dimensional objects by layering thermoplastic filament. In this article, we will delve into the details of the material extrusion process, the different types of materials used in additive manufacturing and their categories, the advantages of the extrusion process, and the various products made by extrusion.
II. What is Material Extrusion in Additive Manufacturing?
Material extrusion is a type of additive manufacturing that uses a thermoplastic filament that is fed through a nozzle to create a 3-dimensional object layer by layer. The filaments are made of different types of materials such as polycarbonate, acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene (ABS), polyethylene terephthalate (PET), and nylon.
III. Material Extrusion in 3D Printing
Material extrusion, an industry-standard 3D printing technology, is a process that is commonly used in the creation of consumer products, professional parts, and prototyping. The process works by heating, melting and extruding polymers layer over layer to fabricate complex shapes.
IV. Materials Used in Extrusion Process
The materials used in material extrusion depend on the product design and specific requirements. Some of the popular materials used in the process include ABS, PLA, TPE (thermoplastic elastomers), Nylon, and PET.
V. Categories of Additive Manufacturing
There are different categories of additive manufacturing that include Material extrusion (FDM/FFF), Vat photopolymerization (SLA/DLP), Binder jetting, Powder bed fusion (SLS/DMLS), Sheet lamination, and Directed Energy Deposition (DED).
VI. Types of Manufacturing Processes
The four types of manufacturing processes are casting and molding, forming, machining, and joining.
VII. Examples of Extrusion Products
There are many products that can be made using the extrusion process, such as plastic tubes for food or medical use, sheets for packaging, window frames, and pipes.
VIII. Other Names of Material Extrusion
Material extrusion is also known as Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF) and Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM).
IX. Products Made by Extrusion
Other products made by extrusion include landscape edging, weather stripping, and electrical conduit.
X. Extrusion in Plastic Manufacturing
Extrusion in plastic manufacturing refers to the process of pushing molten plastic through a die to give it its desired shape.
XI. Types of Extrusion Processes
The two types of extrusion processes are direct extrusion and indirect extrusion.
XII. Advantages of Extrusion
The advantages of extrusion include saving time and money, creating precise products, producing a large volume of products, and improving product quality.
XIII. Conclusion
In conclusion, material extrusion is an essential part of additive manufacturing and 3D printing. The process can be used to create a wide range of products using a variety of materials. The extrusion process offers many advantages and produces products with high precision, low cost, and excellent quality
- Applications of Material Extrusion:
Material extrusion, also known as Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) or Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF), is a widely used 3D printing technology with diverse applications. Some of the key applications of material extrusion in additive manufacturing include:
a. Prototyping: Material extrusion is commonly employed for rapid prototyping to create functional prototypes for testing, design verification, and validation.
b. Manufacturing Tools: This technology is used to fabricate custom manufacturing tools, jigs, and fixtures, which can improve production efficiency and accuracy.
c. Concept Modeling: Material extrusion allows for quick and cost-effective production of concept models, enabling designers to visualize and refine their ideas.
d. End-Use Parts: FDM can produce end-use parts in various industries, such as automotive, aerospace, consumer goods, and healthcare, for applications where the material properties meet the requirements.
e. Education and Research: Material extrusion 3D printers are widely used in educational settings for hands-on learning and research purposes, allowing students and researchers to explore design concepts and practical applications.
f. Architectural Models: FDM technology is utilized in architecture to create precise and detailed scale models of buildings and structures.
- Material Extrusion in Additive Manufacturing Process:
Material extrusion is an additive manufacturing process that involves the deposition of material in a layer-by-layer fashion to build a 3D object. The process begins with a digital 3D model, which is sliced into thin horizontal layers using slicing software. The 3D printer then follows the instructions from the sliced file to deposit or extrude the material, layer by layer, until the entire object is fabricated.
During material extrusion, a thermoplastic filament or other extrudable material is fed into the 3D printer's nozzle. The nozzle, which is typically heated, melts the filament, and the printer's controlled movements precisely deposit the melted material onto the build platform. As each layer is deposited and solidified, the build platform lowers or the nozzle rises to accommodate the next layer, continuing the build process until the object is complete.
- Types of Material Extrusion Additive Manufacturing:
There are several types of material extrusion additive manufacturing technologies, each differing in the specific method of material deposition and the materials used. The main types of material extrusion 3D printing are:
a. Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM): FDM is one of the most widely used material extrusion technologies. It uses thermoplastic filaments as the printing material, and the filament is heated and extruded through a nozzle onto the build platform.
b. Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF): FFF is similar to FDM and often used interchangeably with it. Both FDM and FFF refer to the same process of extruding and depositing thermoplastic materials layer by layer.
c. Robocasting: This variation of material extrusion is specifically used for printing ceramics and other highly viscous materials. It employs a paste-like material that is extruded and deposited to create 3D structures.
d. Direct Ink Writing (DIW): DIW is a material extrusion technique that uses liquid inks or pastes instead of solid filaments. It is commonly used in bio-printing and printing soft materials like hydrogels.
Each type of material extrusion has its unique strengths and applications, making them suitable for various industries and use cases.