Table of Contents:
- Introduction
- The Injection Moulding Process
- Materials Used in Injection Moulding
- Applications of Injection Moulding
- Advantages and Challenges of Injection Moulding
- Future of Injection Moulding
- Conclusion
-
1. Introduction:
Injection moulding is a manufacturing process used to create parts or products by injecting molten material into a mould cavity. It is one of the most widely used manufacturing processes in the world, producing everything from automotive parts to medical devices and consumer goods.
The importance of injection moulding to the manufacturing industry cannot be overstated. It is a highly efficient process that allows for the creation of complex parts at a fast rate and low cost. In this section, we will provide an overview of injection moulding and highlight its importance in the manufacturing industry.
-
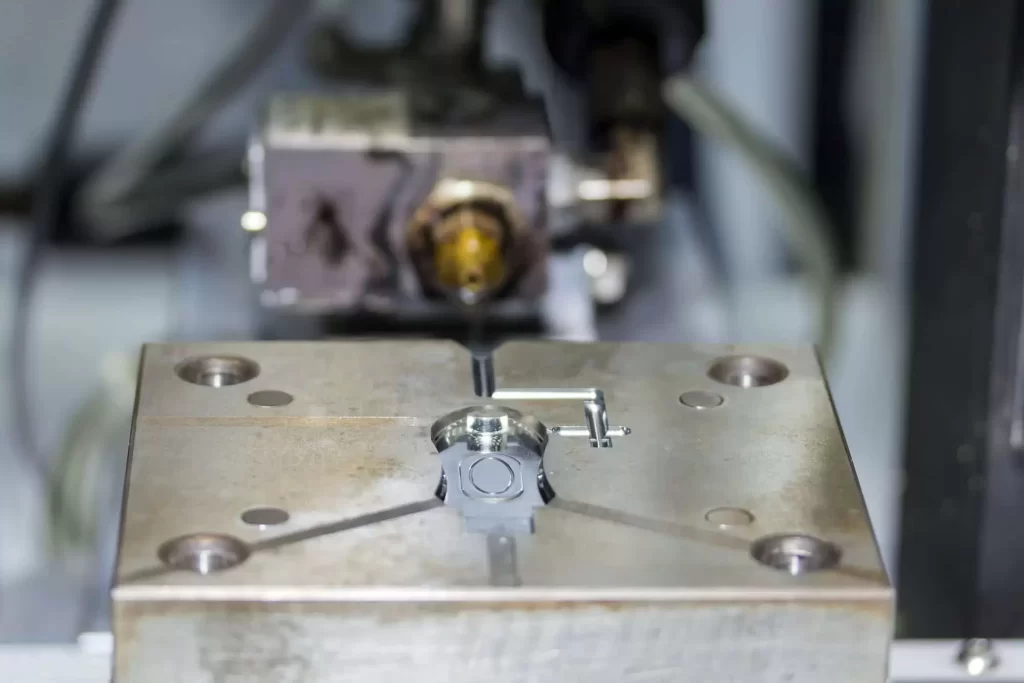
2. The Injection Moulding Process:
Injection moulding is a highly precise manufacturing process that involves the injection of molten material into a mould cavity. Here are the critical aspects of the injection moulding process:
- Description of the Process: The process begins by melting plastic pellets, which are then injected into a mould cavity at high pressure. The molten material cools and solidifies inside the mould, creating the desired shape.
- Machine Components: The main components of an injection moulding machine are the injection unit, the clamping unit, and the control system. The injection unit is responsible for melting and injecting the molten material into the mould. The clamping unit holds the two halves of the mould together and applies pressure during the injection moulding cycle. The control system manages and monitors the process throughout the injection moulding cycle.
- Injection Moulding Cycle: The injection moulding cycle consists of several stages, including material preparation, injection, packing, cooling, and ejection. The duration of the cycle depends on the size and complexity of the part being manufactured, with cycle times ranging from a few seconds to several minutes.
Understanding these critical aspects is essential in achieving consistency and quality in the injection moulding process. With proper control of these factors, manufacturers can produce high-quality parts with precise specifications.
-
3. Materials Used in Injection Moulding:
The materials used in injection moulding are thermoplastics, which can be repeatedly melted and solidified. Here are the critical aspects of the materials used in injection moulding:
- Types of Thermoplastics: There are many types of thermoplastics used in injection moulding, including polypropylene, polyethylene, polystyrene, and acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS). Each type of thermoplastic has unique characteristics that make it suitable for different applications.
- Characteristics of Materials Used: The characteristics of the material used in injection moulding greatly affect the final product’s properties. The material’s melt flow rate, viscosity, and shrinkage rate are essential considerations for achieving precise dimensions and avoiding defects such as warpage and sink marks. Other factors like the material’s strength, stiffness, and heat resistance affect the part’s performance, durability, and suitability for a particular application.
Manufacturers should carefully consider the material properties and choose the appropriate thermoplastic for a particular product to ensure that the final product meets the desired performance requirements. Understanding material characteristics enables manufacturers to optimize injection moulding parameters, achieving consistent quality products during production.
-
4. Applications of Injection Moulding:
Injection moulding has a wide range of applications across various industries, here are some of its applications:
- Automotive: Injection moulding is used to produce various automotive components, including interior and exterior parts such as dashboards, door panels, and bumpers.
- Medical Devices: Injection moulding is widely used in the medical industry to produce disposable medical devices, tools, and equipment such as syringes, test tubes, and catheters.
- Consumer Goods: Injection moulding is used to produce a wide range of consumer goods, including cell phone cases, toys, kitchen appliances, and office equipment.
- Other Industries: Injection moulding is also used in other industries, including aerospace, construction, and electronics manufacturing to produce components and parts used in these industries.
Injection moulding’s versatility and flexibility make it an ideal manufacturing process for many applications, and the ability to produce high volumes of parts at low cost makes it an attractive option for large-scale production.
-
5. Advantages and Challenges of Injection Moulding:
As with any manufacturing process, injection moulding has advantages and challenges. Here are the critical aspects:
1.Advantages:
- High production rates, enabling manufacturers to produce large quantities of parts quickly and efficiently.
- Consistency in part quality, as the injection moulding process can produce parts with tight tolerances and precise dimensions repeatedly.
- Versatility in materials and part design makes it possible to create complex parts with intricate details.
- Low labor cost, as the process can be automated, reducing the need for manual labor.
- Low waste, with the ability to recycle excess material to reduce waste.
.
2.Challenges:
- Initial tooling cost can be high, especially for complex designs.
- Material selection important, as the wrong material properties can lead to defects or part failure.
- Need for precise process control may require skilled technicians and specialized equipment.
- Environmental concerns may arise due to the use of potentially hazardous materials and the generation of plastic waste.
Overcoming these challenges requires careful planning, process expertise, and investment in specialized equipment to ensure optimal performance and maximal output. Successful integration of injection moulding requires an assessment of its unique requirements and alternatives, such as 3D printing or CNC machining, as means to compare, so as to have a clearer view of the most suitable manufacturing process.
-
6. Future of Injection Moulding:
The injection moulding industry is continuously evolving, with technological advancements driving innovation and increasing efficiency. Here are some potential advancements and applications in the future of injection moulding:
1.Technological Advancements:
- Integrating Industry 4.0 technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) could enable real-time monitoring of the injection moulding process, improving efficiency and quality control.
- The development of new materials, coatings and surface treatments that enhance durability, wear resistance and ease of release.
- The application of 3D printing technology to support prototyping, tooling and production in the injection moulding process, offering greater flexibility in design and production.
2.Potential Applications:
- 3D printed moulds for injection moulding, which offers a shorter lead time, reduced cost, and simpler part geometries for constructing mould parts.
- Biodegradable materials for eco-friendly products can replace standard thermoplastic materials, minimizing the environmental impact of plastic manufacturing.
- The ability to manufacture larger parts or products to meet the demand of products for a cost effective production.
These advancements will allow for more efficient, cost-effective, and eco-conscious manufacturing in the future of injection moulding. Well-designed parts with optimized materials, and precise manufacturing can have a significant impact on the functionality of a product. Therefore, the advancement of technology will enable more advanced manufacturing across various industrial sectors that depend on this manufacturing technology.
If you need about injection moulding Services,You can click on the V1 Prototype website to find it.
-
7. Conclusion
Injection moulding is a widely used manufacturing process that produces high-quality parts and products at low cost and high volume. The versatility and flexibility of injection moulding have enabled its use in various industrial sectors, including automotive, medical, and consumer goods.
Injection moulding’s future looks bright with advancements in technology, such as 3D printing, and Industry 4.0 technologies such as AI and the IoT, will enhance the manufacturing process. Additionally, eco-friendly materials will promote sustainability and address environmental concerns.
Overall, injection moulding is a reliable and cost-effective manufacturing process that will continue to play a pivotal role in the manufacturing industry’s growth. As technology continues to advance and eco-friendly materials are increasingly integrated into the process, injection moulding will continue to evolve and improve, providing better products at a lower cost.