Table of Contents:
- Introduction to Injection Moulding Die
- The Injection Moulding Process
- Types of Injection Moulding Dies
- Materials Used for Injection Moulding Dies
- Designing Injection Moulding Dies
- Understanding Injection Moulding Die Maintenance
- Troubleshooting Common Injection Moulding Die Problems
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Injection Moulding Dies
- Future of Injection Moulding Die Technology
- Conclusion: The Importance of Injection Moulding Dies in the Manufacturing Industry.
-
1.Introduction to Injection Moulding Die
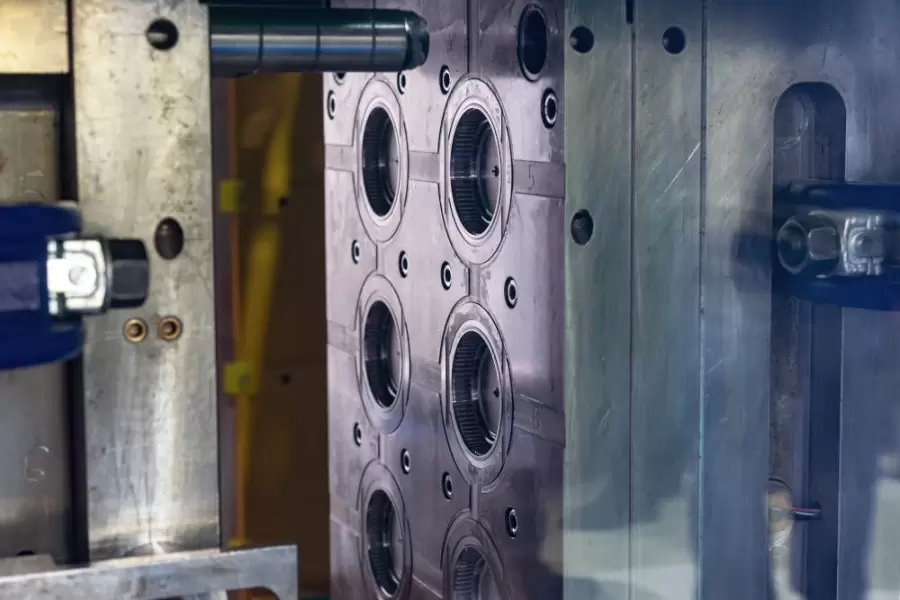
Injection moulding is a widely used manufacturing process that involves injecting molten material, typically thermoplastics, into a mould to form a specific shape. The injection moulding die is the critical component that determines the shape and quality of the final product. Understanding the different types of injection moulding dies, materials used in their construction, and how to design and maintain them is critical to the success of any injection moulding process.
-
2.The Injection Moulding Process
The injection moulding process involves four major steps:
- Material preparation - the material, typically in the form of pellets, is melted and compressed into a cylinder.
- Injection - The molten material is injected into the mould cavity using high pressure.
- Cooling - The material solidifies in the mould, which is then cooled to facilitate removal of the final product.
- Ejection - The mould is opened, and the final product is ejected.
-
3.Types of Injection Moulding Dies
There are several types of injection moulding dies, including:
- Two-plate mould - It consists of a stationary plate and a moveable plate that are mounted on opposite sides of the die.
- Three-plate mould - It has an additional plate, which serves to separate the runner system and the part.
- Hot runner mould - This type of mould keeps the plastic in the runner system molten, reducing waste and cycle time.
- Multicavity mould - It allows multiple identical parts to be produced simultaneously, increasing production efficiency.
-
4.Materials used for Injection Moulding Dies
Injection moulding dies are typically made from steel, with various grades of steel used depending on the complexity and durability requirements of the mould. Common types of steel used are P20, H13, and S136. Additionally, aluminium and copper alloys may be used for low-volume production because of their thermal conductivity and ease of machining.
-
5.Designing Injection Moulding Dies
Designing an injection moulding die requires careful consideration of several factors, including the material to be used, the shape and size of the part, and the number of cavities needed. 3D modeling software is often used to design the die and simulate the injection moulding process to identify issues that may arise.
-
6.Understanding Injection Moulding Die Maintenance
Regular maintenance is necessary to ensure the longevity and efficiency of an injection moulding die. Maintenance tasks include regular cleaning, lubrication, and inspection for signs of wear and damage. Any issues identified should be addressed promptly to prevent production downtime and reduce the risk of equipment failure.
-
7.Troubleshooting Common Injection Moulding Die Problems
Common issues encountered in injection moulding include flash, sink marks, warpage, and short shots. Flash refers to excessive material protruding from the part due to misalignment of the mould plates. Sink marks occur when uneven cooling results in depressions on the surface of the part. Warping occurs when the moulded part distorts during the cooling phase. Short shots result from insufficient material injected into the mould. Identifying and addressing these issues quickly is critical to maintaining production efficiency and producing high-quality parts.
-
8.Advantages and Disadvantages of Injection Moulding Dies
The primary advantage of using injection moulding dies is the ability to produce large volumes of identical parts at high speed and with high precision. Another significant advantage is the ability to produce complex shapes that would be difficult or impossible to achieve using other manufacturing processes. However, there are some disadvantages to consider, such as the high initial cost of the injection moulding machine and tooling, the need for skilled operators and maintenance personnel, and the potential for equipment and part failures.
-
9.Future of Injection Moulding Die Technology
Injection moulding technology is constantly evolving, with new materials, machine designs, and software tools being developed to improve efficiency, reduce waste, and enhance product quality. One area of growing interest is additive manufacturing, which involves the use of 3D printing to produce the moulds themselves. Additive manufacturing could significantly reduce the cost and time required to produce custom moulds, and also enable increased flexibility and design freedom.
Click on the V1 Prototype website to gain more information.
-
10.Conclusion: The Importance of Injection Moulding Dies in the Manufacturing Industry
Injection moulding dies play a critical role in the manufacturing industry, allowing for the efficient and cost-effective production of high-quality parts. Understanding the different types of injection moulding dies, materials used for their construction, and how to design and maintain them is crucial for businesses that rely on this manufacturing process. By staying up-to-date with the latest injection moulding technologies and techniques, manufacturers can continue to produce high-quality parts that meet or exceed customer expectations.
Injection molding is a highly versatile and widely used manufacturing process for producing plastic parts and products with precision and efficiency. Central to this process is the injection molding die, a critical tool that plays a pivotal role in shaping the final product. The injection molding die, also known as the mold, is a custom-designed tool that contains cavities and channels through which molten plastic is injected at high pressure. It is crafted with meticulous attention to detail, taking into account factors such as material selection, product design, cooling channels, and ejection mechanisms. The quality and precision of the injection molding die directly impact the quality and consistency of the molded parts. As a result, manufacturers must carefully consider factors such as die material, tooling technology, and maintenance to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Successful injection molding relies on a comprehensive understanding of the injection molding die and its intricate workings. The die design must be tailored to meet the specific requirements of each project, encompassing factors like part complexity, undercuts, and draft angles. Manufacturers must also consider factors that affect cycle times, such as cooling systems that efficiently extract heat from the molten plastic. Furthermore, the material selection for the die itself is crucial, as it must withstand the high temperatures and pressures of the injection molding process while resisting wear and tear. Regular maintenance and proper storage of the injection molding die are equally vital to extend its lifespan and prevent costly downtime.
In conclusion, the injection molding die is the backbone of the injection molding process, and its significance cannot be overstated. A well-designed and meticulously crafted die ensures the production of high-quality plastic parts with consistency and efficiency. Manufacturers and industry professionals must continuously stay abreast of the latest advancements in die technology, materials, and maintenance practices to optimize production and remain competitive in the dynamic world of plastic manufacturing. With the proper knowledge and attention to detail, injection molding dies contribute to the creation of a diverse range of plastic products that impact numerous sectors, from automotive and electronics to medical and consumer goods.